Overlapping
Overlapping peptide libraries are ideal for T-cell epitope searching, because T cell epitopes are by nature short linear peptides from the primary protein sequence. They are also appropriate for scanning the primary sequence of proteins for linear, or "continuous”, B-cell (antibody-defined) epitopes.
Truncation
Truncation peptide libraries are used to identify the shortest amino acid sequence needed for activity. The library is constructed by systemically removing the flanking residues of the original peptide. If the essential amino acids are known (eg. by Alanine Scanning), the direction of truncation can be tailored to maintain these residues, whilst truncating the opposite end.
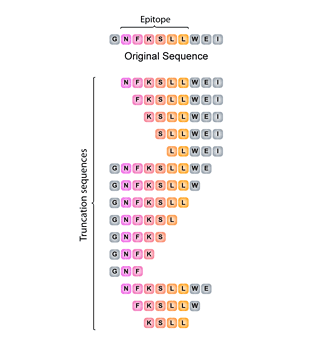
T-cell Truncated
Truncated peptide libraries allow the testing of all possible T-cell epitopes (ie. all 8 to 11-mers) across a protein of interest. In each tube, we provide equimolar mixtures of the four C-terminal peptides for each nominal 11-mer. After screening, positive tubes can be deconvoluted for precise epitope identification.

Alanine Scan
Alanine Scanning is able to identify specific amino acid residues responsible for a peptide's activity. Alanine is used to substitute each residue sequentially.
Substitution of an essential amino acid results in a reduction in peptide activity, with the degree of activity reduction taken as a relative measure of the importance of the amino acid being substituted.

Positional Scan
Positional scanning is an important tool for peptide sequence optimization. This identifies an amino acid of interest at a single position and substitutes it with all other natural amino acids one at a time. Increases in activity will identify the preferred amino acid residues at this positions.

Combinatorial 2-Positional Scan
Positional scanning is an important tool for peptide sequence optimization. Two position combinatorial scanning identifies amino acids of interest at two given positions and substitutes them with all other natural amino acids one at a time. Increases in activity will identify the preferred amino acid residues at these positions.

Combinatorial 3-Positional Scan
Positional scanning is an important tool for peptide sequence optimization. Three position combinatorial scanning identifies amino acids of interest at three given positions and substitutes them with all other natural amino acids one at a time. Increases in activity will identify the preferred amino acid residues at these positions.

Scrambled
Scrambled libraries are constructed through permutation of the original peptide sequence. They are typically used as:
1. Negative controls to show that a specific sequence rather than the amino acid composition is critical for activity; or
2. A tool for finding new leads by creating a random screening library.




